fungi life cycle explained
As part of their life cycle fungi produce spores. The species of dimorphic fungi belong to the phylum Ascomycota and all are thermally dimorphic except Coccidioides immitis.

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts
Spore germ hypha mature mycelium.

. The Life Cycle of Fungi There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. Macroscopic filamentous fungi that form large fruiting bodies. The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting body the part of a mushroom we all identify and know that releases new spores to create a new cycle all over again.
The dimorphic fungi exist in two forms at different environment temperature oxygen concentration etc. Asexual reproduction takes place by uninucleate thin-walled spores which are referred to as conidia. In this electron micrograph of a mushroom gill the four spores produced by meiosis seen in the center of this picture are carried on a clublike sporangium visible to the left and right.
But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death. Fungi can reproduce asexually by budding and many also have sexual reproduction and form fruitbodies that produce spores. Most of the ecology of the soil will die the plants do ok in the short run as they are able to absorb from the dead bacteria and fungi but it is a slow cycle of death.
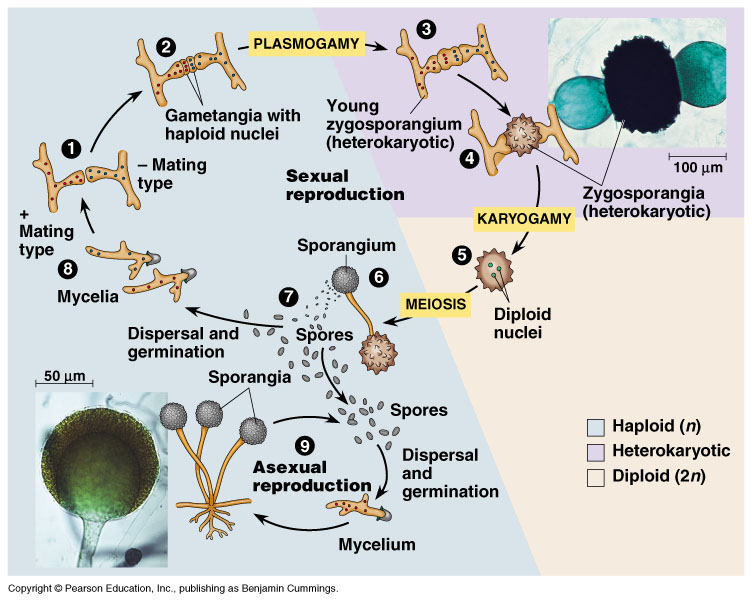
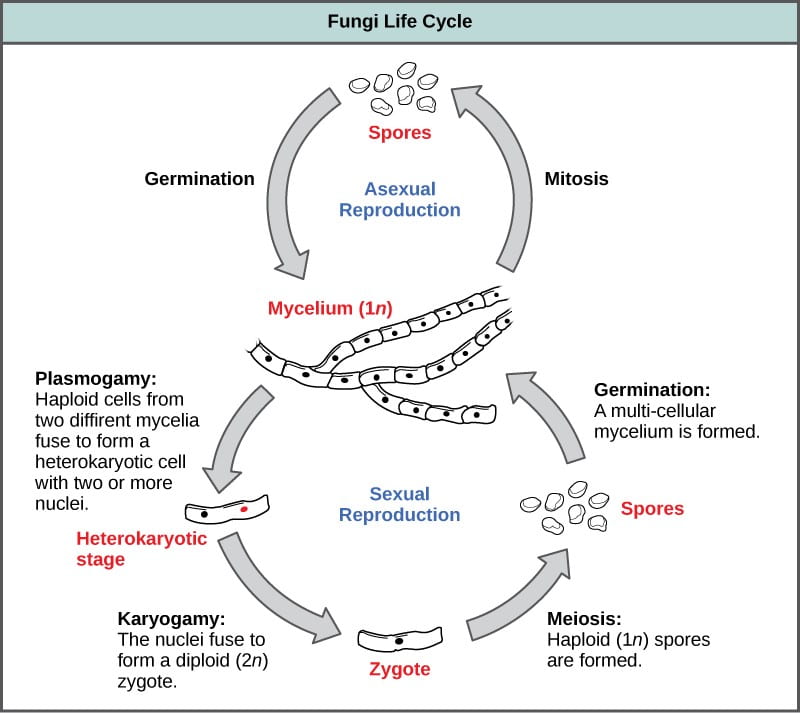
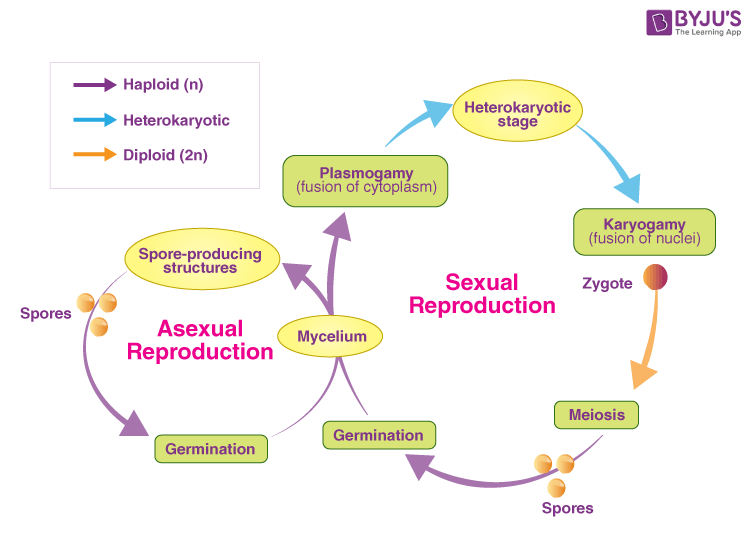
Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular. The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two. Mature mycelium In reality there are many sub-steps of the process.
Fungus are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs cannot make their own food and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria. This is how the fungus reproduces asexually.
2022 Fungi Perfecti LLC PO Box 7634 Olympia WA 98507 USA. The mycelium in most species of Taphrina is annual but in some species it is perennial. Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores reproductive or distributional cells they produce.
Order Toll Free US Canada. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative diagram of the developmental stages of a mould. But this model provides a good overview in terms of how fungi grows from birth to death.
The three major groups of fungi are. These spores also contain enough nutrients to support germination when it occurs. However they are also responsible for some.
They may be unicellular or filamentous. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms. They reproduce by means of spores.
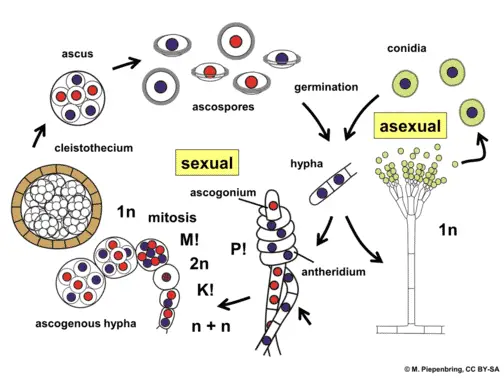
The conidia are developed from the ascospores. Most fungi are microscopic but many produce the visible fruitbodies we call mushrooms. The majority of mold fungi do not have sexual stages and following this simple life cycle pattern.
The stage during which a fungus reproduces asexually is known as asexual stage or asexual. For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. Life cycle of fungi.
In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. Life Cycle of Fungi Some of the characteristic features of fungi are. The life cycle inventory phase involves the compilation of elementary flow data ie flows that pass.
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells. They are eukaryotic non-vascular non-motile and heterotrophic organisms. And the property exhibited by them is known as dimorphism.
Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the. Fungi exist primarily as filamentous dikaryotic organisms. Once the spores are mature the mushroom releases them into the air.
They lack chlorophyll and thus are incapable of photosynthesis. The mushroom life span varies between fungi species. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi.
They then travel on the wind until they land on an appropriate surface and start the cycle again. They exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. Filamentous and yeast-like phases are seen in their life.
Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation. If this is a. In these cells genetic material from the parent fungi combines and divides to form spores.
Fungi life cycle explained Wednesday March 2 2022 Edit. During sexual reproduction the changes involved in the process occur in regular sequence in cyclic order. Fungi reproduce sexually either through cross- or self-fertilization.
The ascospores produce conidia by budding.
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

Life Cycle Of Aspergillus And Suggested Localization Of Ribotoxins Download Scientific Diagram

Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle
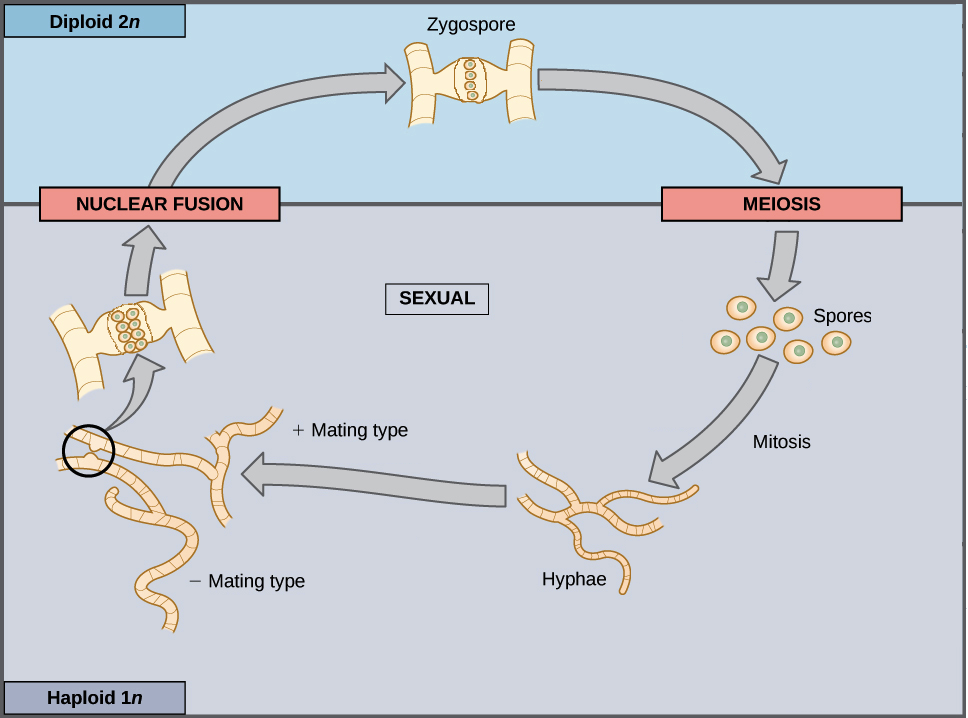
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy

Characteristics Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e
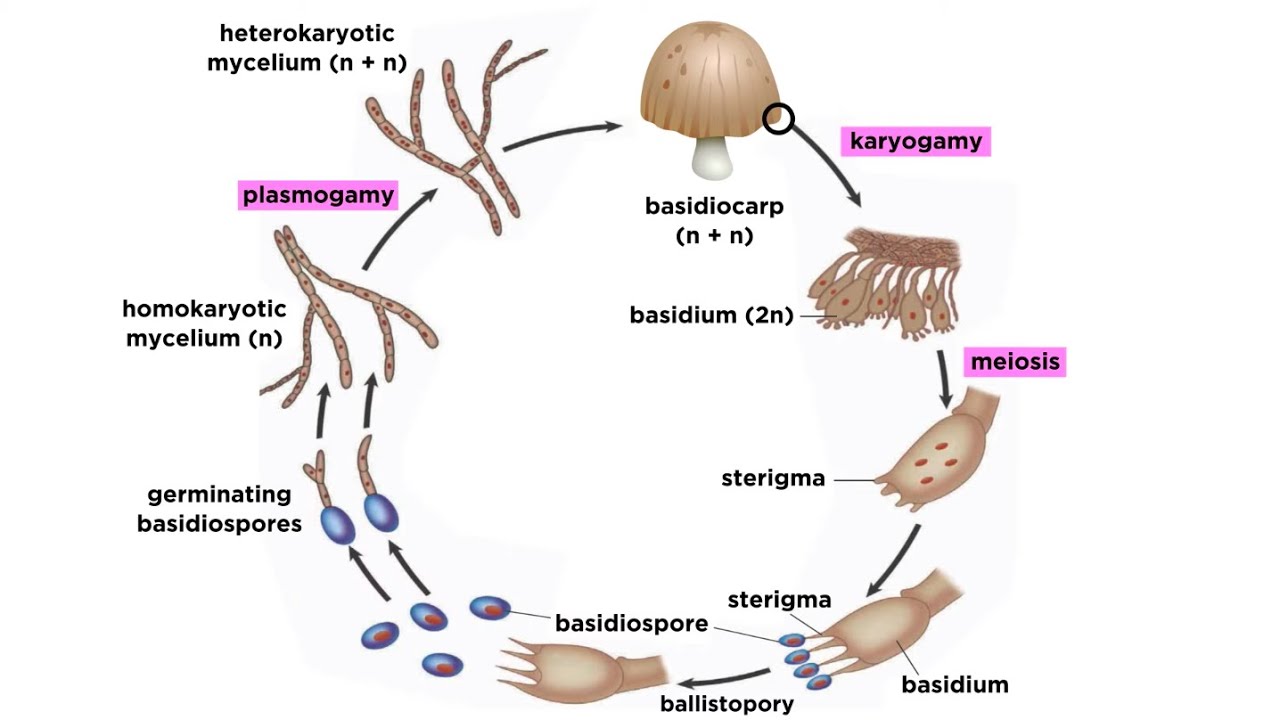
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

Biology Pictures Fungi Life Cycle 3 Life Cycles Fungi Biology

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii